Let’s know about Tobacco beetle
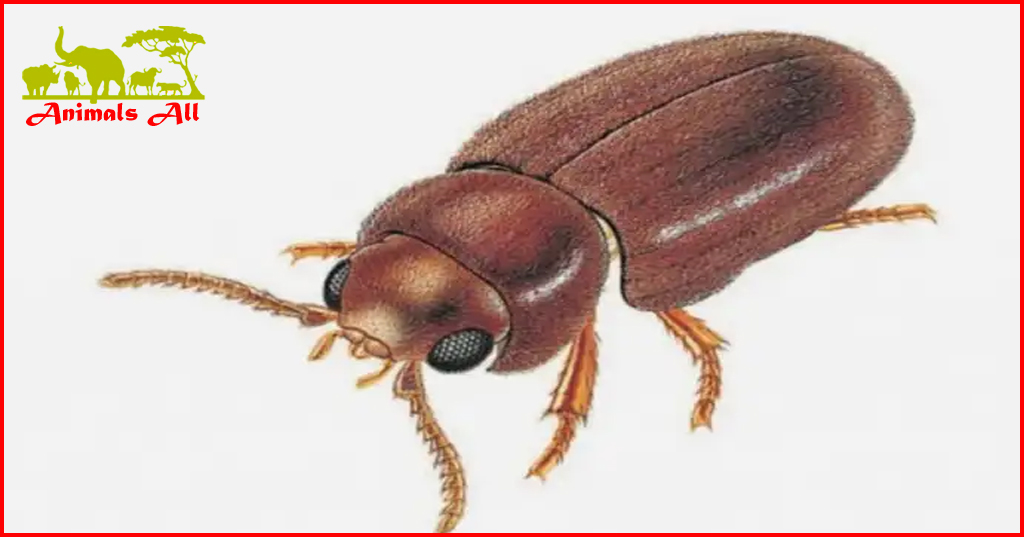
The tobacco beetle ( Lasioderma serricorne ) is a species of hairy beetle in the family Lasioderma, superfamily Lasiodermoidea, order Coleoptera. It is 2-3mm long, brown, and has the ability to fly. The tobacco beetle has a wide range of food. In addition to tobacco leaves and cigarettes, it mainly harms stored grains, beans, and dried fruits. Both the adult and larvae of the tobacco beetle can drill into the grain and devour the germ and endosperm, causing the grain to deteriorate in quality, lose nutrients, and become moldy and deteriorate.
The optimal development conditions for tobacco beetles are a temperature of 30°C and a relative humidity of 70%. The female lays about 100 eggs each time. After hatching, the larvae feed on the material where the eggs are located. They generally need to molt four times before pupating. Adults do not eat and have a lifespan of 2-6 weeks. Tobacco beetles are not cold-resistant. In an environment of 4°C, most adults will die within 6 days; and eggs will die after 5 days in an environment of 0-5°C.

The harm of tobacco beetles to food in the family is mainly manifested in the following aspects:
1. Destroy the quality and nutritional value of food
The larvae and adults of tobacco beetles will chew on the surface or inside of grains, causing them to deform, change color, taste, and deteriorate, reducing their quality and nutritional value.
2. Spread bacteria and fungi
The body surface and excrement of tobacco beetles carry bacteria and fungi, which can contaminate food, causing it to mold, deteriorate, and stink, increasing food losses.
3. Produce harmful substances
When tobacco beetles move in grains, they will produce some harmful substances such as organic acids, esters , aldehydes, etc., which will affect the aroma and taste of grains and even cause harm to human health.
Prevention and control measures:
1. When storing grain, pay attention to sealing, drying, cleaning, and ventilation to avoid factors that are conducive to the growth of tobacco beetles, such as excessive humidity, high temperature, or too much debris.
2. Check the stored grain regularly and deal with any signs of tobacco beetles or other pests promptly , remove dead insects, eggs, feces and other contaminants, and wipe the storage containers with warm water or alcohol.
3. Use physical or chemical methods to control tobacco beetles: Physical methods include using yellow plastic sheets or pheromone traps to capture adult beetles; chemical methods include various special insecticides on the market. Read the instructions carefully before use to avoid contamination to yourself, others, and the environment.


One thought on “Let’s know about Tobacco beetle”